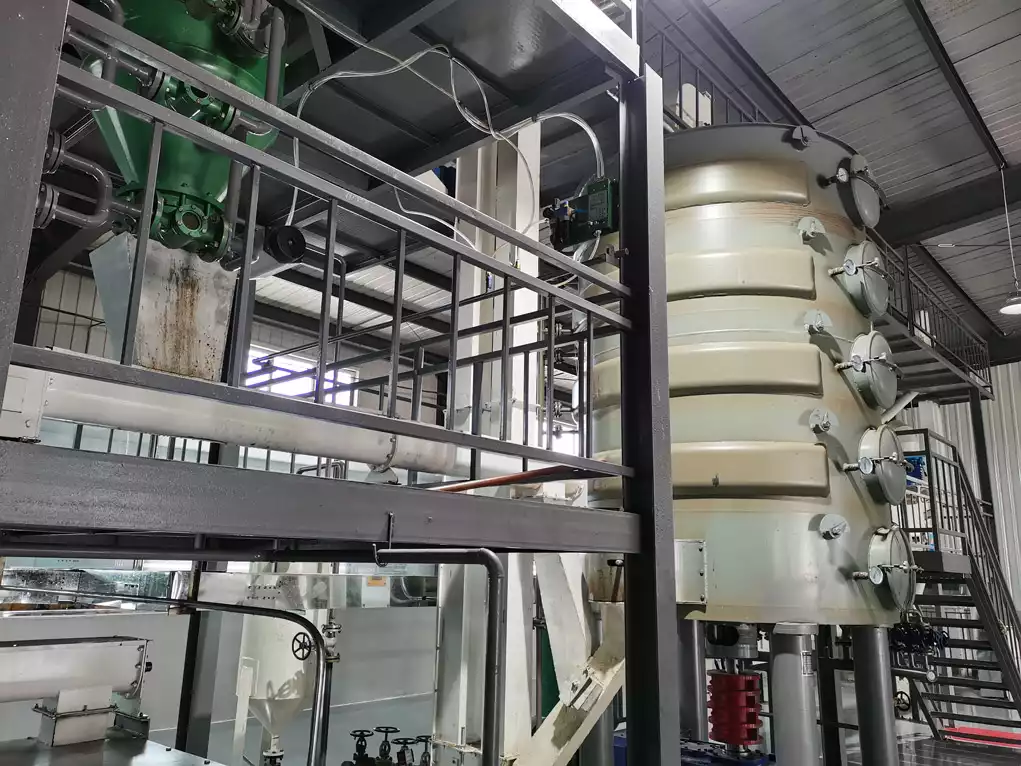
Introduction
Peanut oil is a common edible oil, which is made from a large number of peanut seeds through careful processing. The peanut oil production process involves crushing, pressing, extracting, and refining the peanut seeds using various types of machinery.
Peanut oil is light yellow and transparent, with a clear color, fragrant smell, and delicious taste. It is a relatively easy-to-digest edible oil. Groundnut oil contains more than 80% unsaturated fatty acids (including 41.2% oleic acid and 37.6% linoleic acid). It also contains 19.9% saturated fatty acids such as palmitic acid, stearic acid, and arachidic acid.
Eating peanut oil can decompose cholesterol in the human body into bile acid and excrete it from the body. Thereby reducing the cholesterol content in plasma. In addition, it also contains substances that are beneficial to the human body, such as sterols, wheat germ phenol, phospholipids, vitamin E, choline, etc. Regular consumption of groundnut oil can prevent skin wrinkling and aging. Protect blood vessel walls, prevent thrombosis, and help prevent arteriosclerosis and coronary heart disease. The choline in peanut oil can also improve human memory and delay brain function decline.
Step1: Raw Material Preparation
The raw material for peanut oil is peanuts. You should choose fresh, mold-free, and pest-free peanuts as raw materials. If using substandard peanuts will affect the quality of the final oil.
Step2: Screening Treatment
Use a grading screen to separate the imperfect peanuts such as immature, mildewed, and broken peanuts from the peanuts, and remove impurities and unqualified peanuts. This part can produce Level 2 peanut oil and sold separately. (Read more: groundnut cleaning sieve >>)
Step3: Baking Treatment
The peanuts after screening need to be baked. The purpose of baking is to remove the peanut shells and increase the oil content of peanuts. Generally, use indirect roasting. Place the peanuts in a baking machine and bake evenly through the action of hot air.
Control the baking temperature at about 120°C and the time is about 30 minutes. After drying, control the moisture content of the peanuts at 5%~6%. Then quickly use cold air to reduce the temperature of the oil particles to below 40°C.
Step4: Shell Removal
After roasting, the shells of the peanuts have become fragile and are shell by a shelling machine. The shelling machine uses the principle of friction grinding to rub the peanuts with the shells, so that the peanut shells break and fall off, thus obtaining the shelled peanut kernels. (Read more: peanut sheller machine >>)
Step5: Cleaning Treatment
Clean the shelled peanut kernels to remove the residual shells and impurities. The cleaning is generally done by water washing. Place peanut kernels in the cleaning pool and washed by water flow to ensure the cleanliness of the peanut kernels.
Step6: Crushing and Peeling
Crush the cleaned peanut kernels. The purpose of crushing is to remove the red skin and better release the peanut oil. Crushing generally uses a roller crusher to put the peanut kernels into the crusher. Crush into small particles by rolling to increase the contact area and improve the oil release rate. After crushing, the red skin is sucked out by a wind air selector or a suction flat screen. The separated peanut red skin uses a pharmaceutical chemical raw material.
Step7: Drying Treatment
The crushed peanut particles contain a certain amount of moisture and need to be dried. The purpose of drying is to remove moisture from the peanut particles and increase the oil content of the peanuts. Generally, use the dryer to dry. Place peanut particles in the dryer and through hot air evaporate the water. Control the drying temperature at about 80°C and the time is about 20 minutes. (Read more: groundnut dryer machine >>)
Step8: Hot Air Baking
After drying, 25%~30% of the total peanut petals are sent to the hot air baking furnace, where the oil is heated to 180°C~200°C. Baking temperature is the key factor in the aroma of fragrant peanut oil. If the temperature is too low, the aroma is weak. If the temperature is too high, the oil is easy to gelatinize.
Step9: Cooling and Crushing
To prevent the oil material from charring and spontaneous combustion, quickly cool it after baking. After cooling, roll the material into small particles using a toothed roller crusher.
Step10: Steaming and Frying
Use a five-layer vertical cooker machine to steam and fry the peanut blanks. The 1st to 2nd layers should be full to play the role of steaming. The 3rd to 5th layers should be shallow to remove moisture. The discharge temperature is 108℃~112℃, and need to control the moisture content at 5%~7%. To ensure that the peanut oil has a rich flavor, the indirect steam pressure of the steaming boiler should not be less than 0.6mpa.
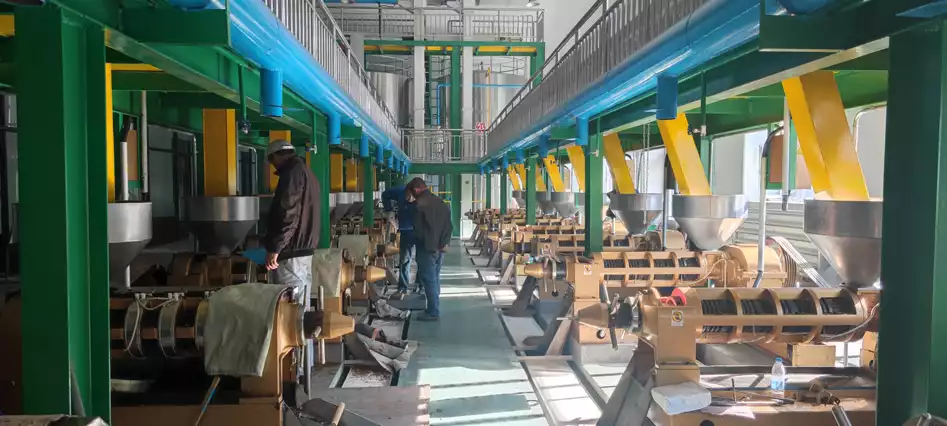
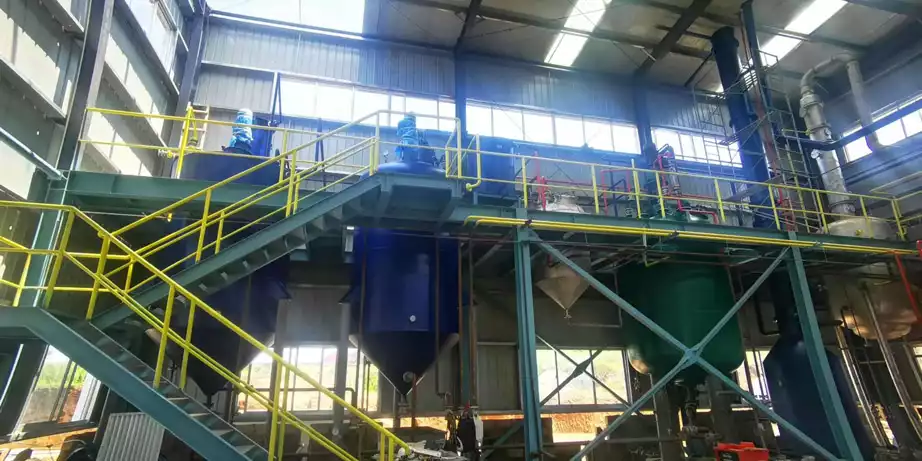
Step11: Pressing Oil
This process uses a YZYX130DJ screw oil press. Considering the particularity of the peanut oil production process, adjusting the spindle speed of the oil press. The spindle speed is increased from the original 8rpm to 10rpm, and the thickness of the thick cake is appropriately increased, generally controlled at about 10mm. Control the inlet temperature at 135℃, the inlet moisture is 1.5%~2%, and the residual oil in the machine-pressed cake is as low as 9%~10%. (Read more: peanut oil extraction machine >>)
Finally, filter the crude oil obtained from pressing using a vertical blade filter and send it to the refining workshop. Crush the pressed cake and send it to the extraction workshop for secondary extraction. The crude oil obtained from extraction can be refined and sold as ordinary oil.
Step12: Solvent Extraction (Optional)
Perform secondary extraction on the crushed pressed cake to extract the peanut oil. Generally, uses oil solvent extraction, where the pressed cake is in an extraction tank, and a food-grade solvent. The oil is dissolved by soaking and stirring, forming a peanut oil solution.
Step13: Desolventizing
Desolventize the crude oil obtained from pressing and the peanut oil solution obtained from extraction to remove any remaining solvent. Heat the peanut oil solution to boiling, causing the solvent to evaporate. The evaporated solvent is then condensed and recovered, resulting in desolventized groundnut oil.
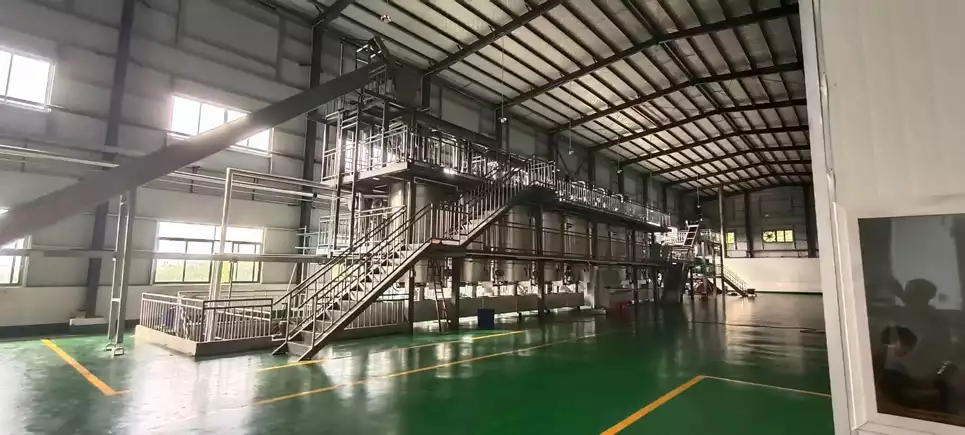
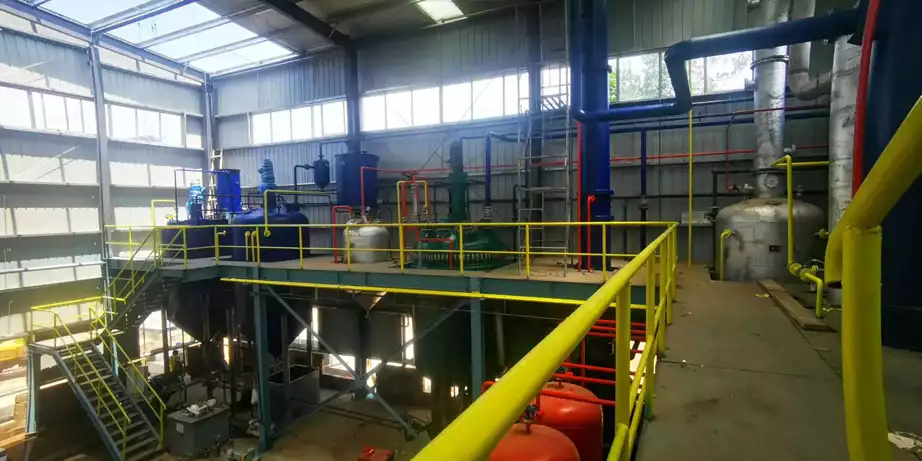
Step14: Deacidification
The peanut oil after desolventization contains certain acidic substances and needs to be deacidified. Deacidification is generally carried out by alkali refining, adding edible alkali, and neutralizing the acidic substances by acid-base neutralization reaction. Then separate the precipitate and alkali solution by centrifugation to obtain deacidified groundnut oil. (Read more: deacidification tower >>)
Step15: Decolorization
The groundnut oil after deacidification is darker in color and needs decolorization. Generally, we use white clay decolorizer for decolorization. Adding an appropriate amount of activated white clay, and removing pigments and impurities by adsorption. Then separate the decolorant and the oil to obtain decolorized peanut oil. (Read more: decolorization tower >>)
Step16: Deodorization
The decolorized groundnut oil contains certain odor substances and needs deodorization. Deodorization generally evaporates the odor substances by distillation and then collects and recycles the evaporated odor substances to finally obtain deodorized peanut oil. (Read more: deodorizing tower >>)
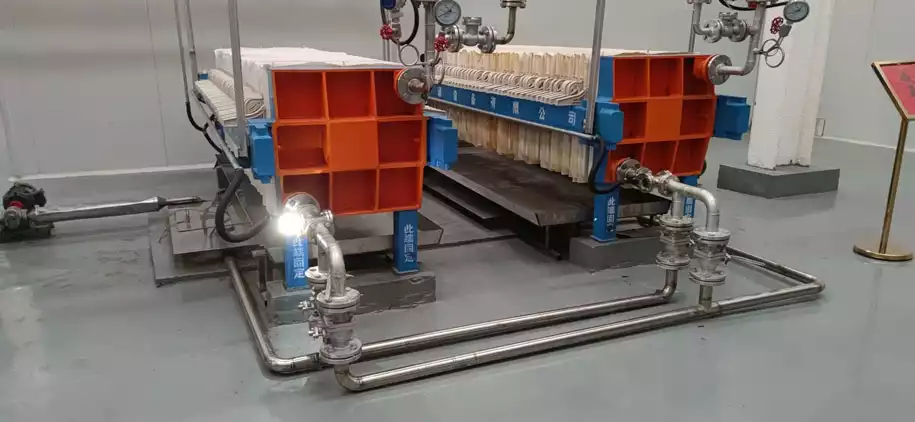
Step17: Filtering
There may still be tiny impurities and sediments in the deodorized peanut oil. You need to filter it. Generally, use a filter press, where the groundnut oil is filtered through a filter cloth to remove any remaining impurities and sediments, resulting in pure peanut oil.
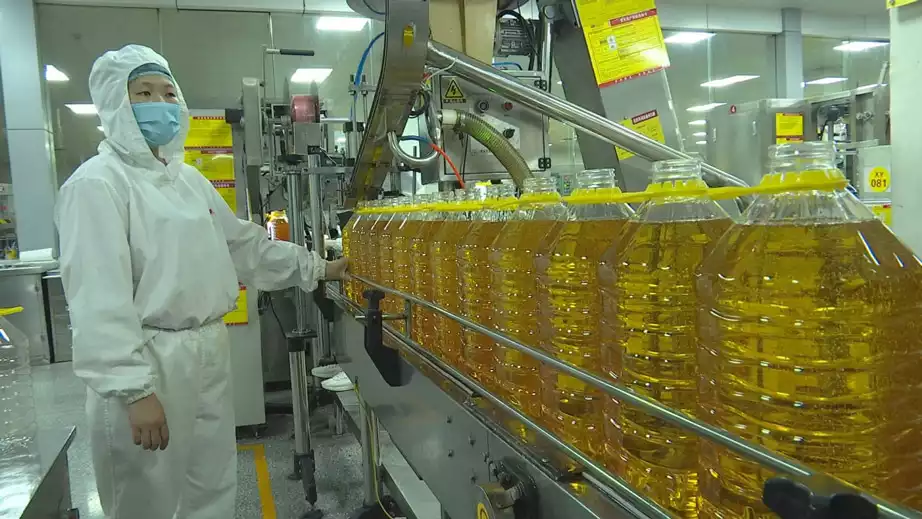
Step18: Packaging and Delivery
Package the filtered peanut oil for sale. Generally, use food-grade plastic barrels or bottles, where the groundnut oil is poured into the packaging containers and sealed, resulting in the finished peanut oil product.
Conclusion
This is the production process of peanut oil. Through a series of processing steps, raw peanuts are transformed into high-quality edible oil. Huatai Oil Machinery provides customized plans for you to help build your business in edible oil processing plants such as peanut, soybean, palm kernel, cottonseed, etc. The full set of oil mills we provide guarantees high quality, low prices, and high oil production. If you are interested, please contact us at 0086-159-3728-9608!
Get your best price
- Engineer quick quote
- The overall delivery speed is fast
- Financial choice
- Low installation costs and cost savings
30 years+ of oil mill plant R&D
More than 56 innovative technologies