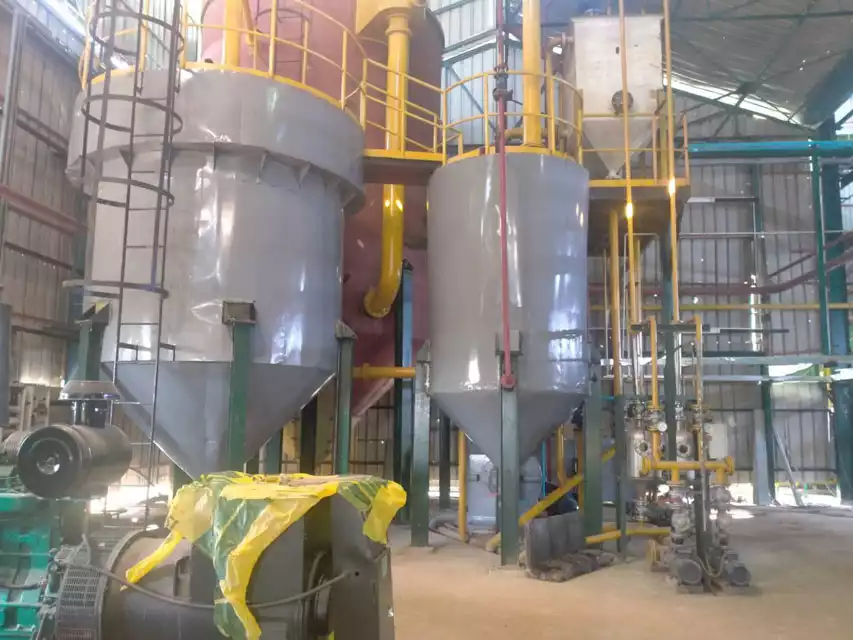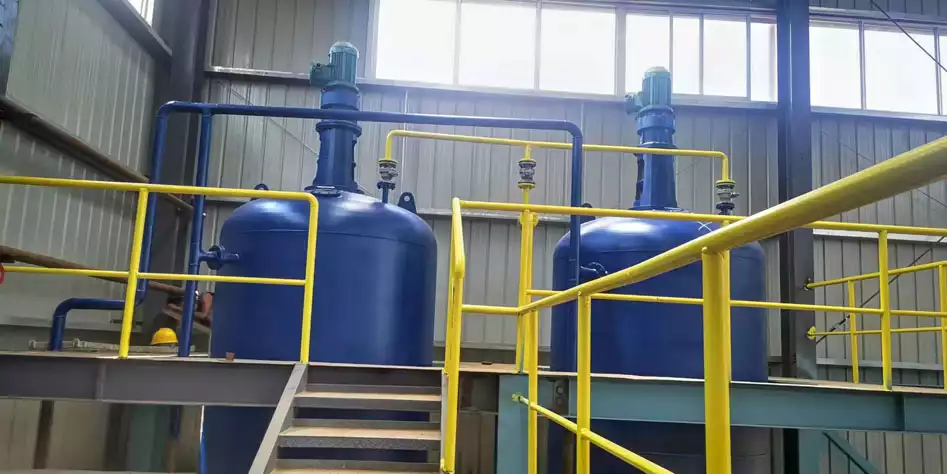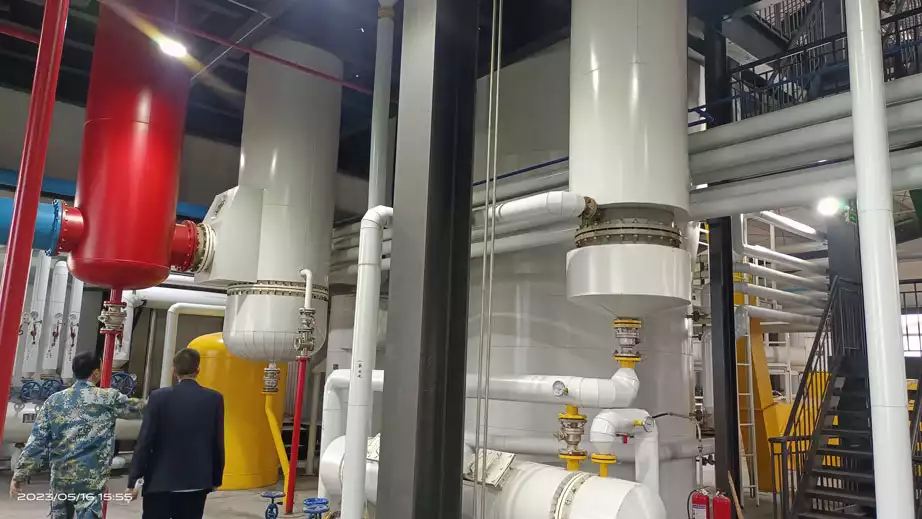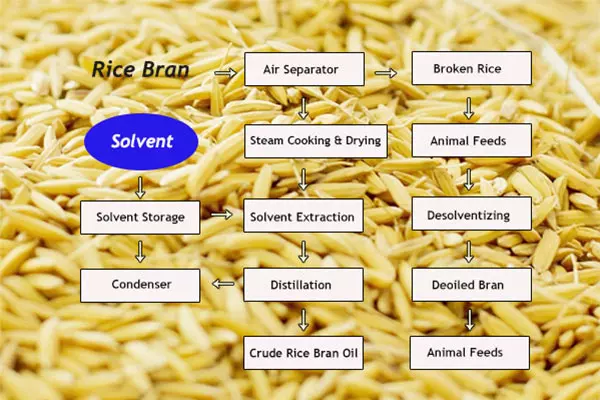
Rice bran oil is an edible oil extracted from rice bran, a byproduct of rice processing. The commonly used methods for making rice bran oil are oil press pressing and extraction equipment extraction.
Because rice bran has a low oil content and is prone to rancidity. So, the cost of producing rice bran oil by pressing is high and the output is low. Therefore, most rice bran oil processing plants use extraction equipment to produce oil. In this article, we will introduce the complete process of rice bran oil production in detail.
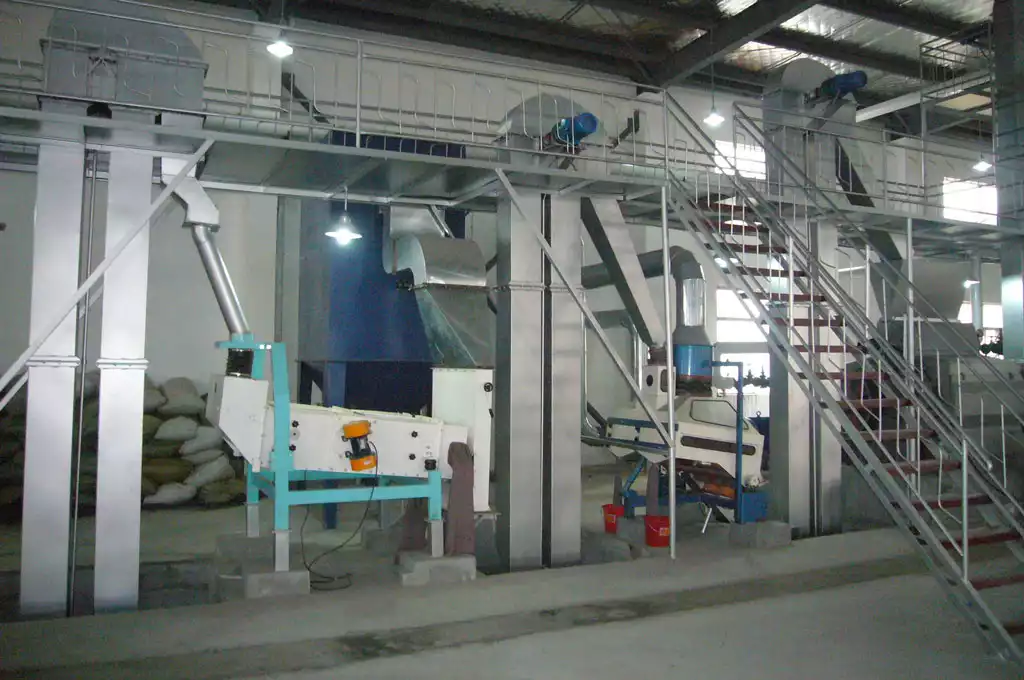
- Rice Bran Pretreatment
Since the raw rice bran contains a small amount of impurities, it needs to be screened and removed. Then it enters the conditioning system. And introduces into the raw material a small amount of steam (about 2% of the raw material). To it soften, to facilitate the subsequent pressing of oil.

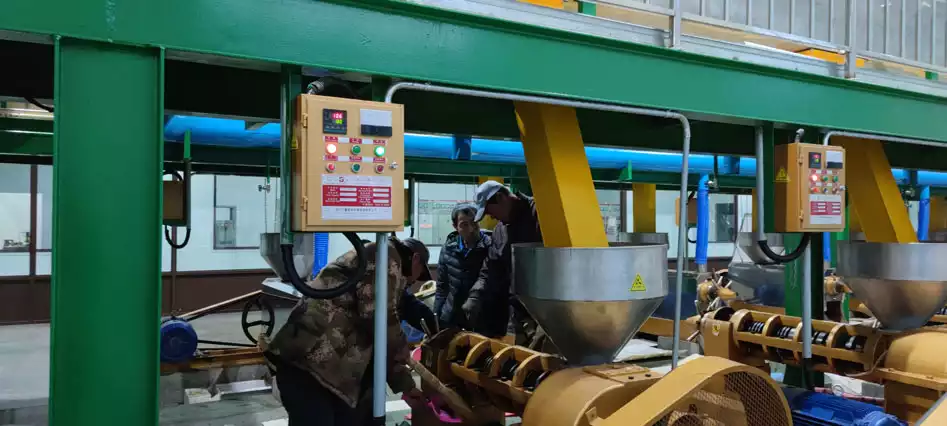
- Pressing
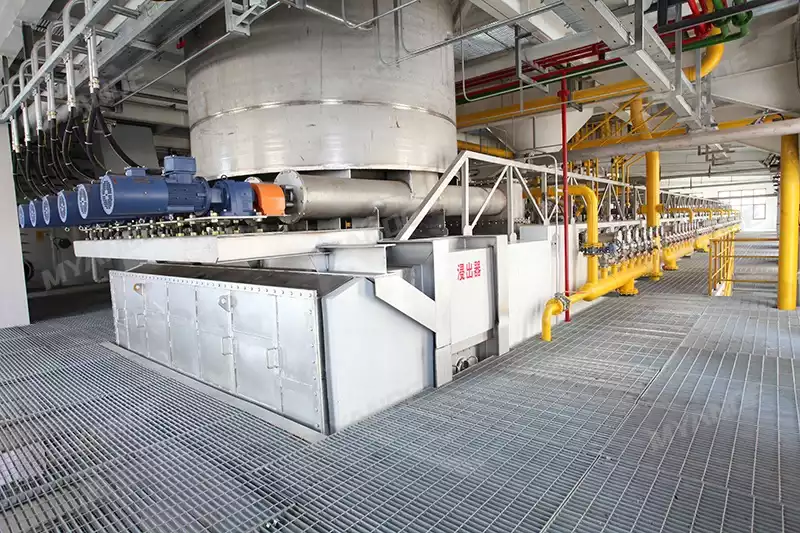
After pretreatment, the rice bran goes directly into the hydraulic oil press. This step extracts most of the oil from the rice bran. The resulting crude rice bran oil can then go straight to the physical refining workshop for purification. However, the pressed cake still contains some crude oil, which we need to extract further in the extraction workshop. (Read more: rice bran oil press machine >>)
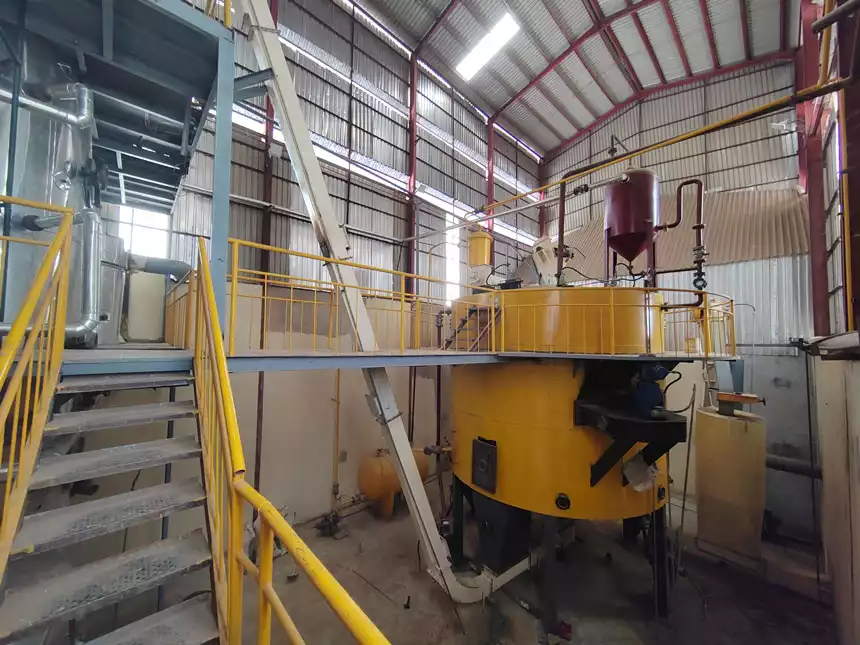
- Solvent Extraction
The cake enters the oil extractor, where we add the solvent n-hexane. The oil in the cake dissolves in the solvent, forming a mixed oil. This mixed oil passes through a filter, which removes the solid meal, resulting in a cleaner mixed oil. (Read more: rice bran oil solvent extraction process >>)
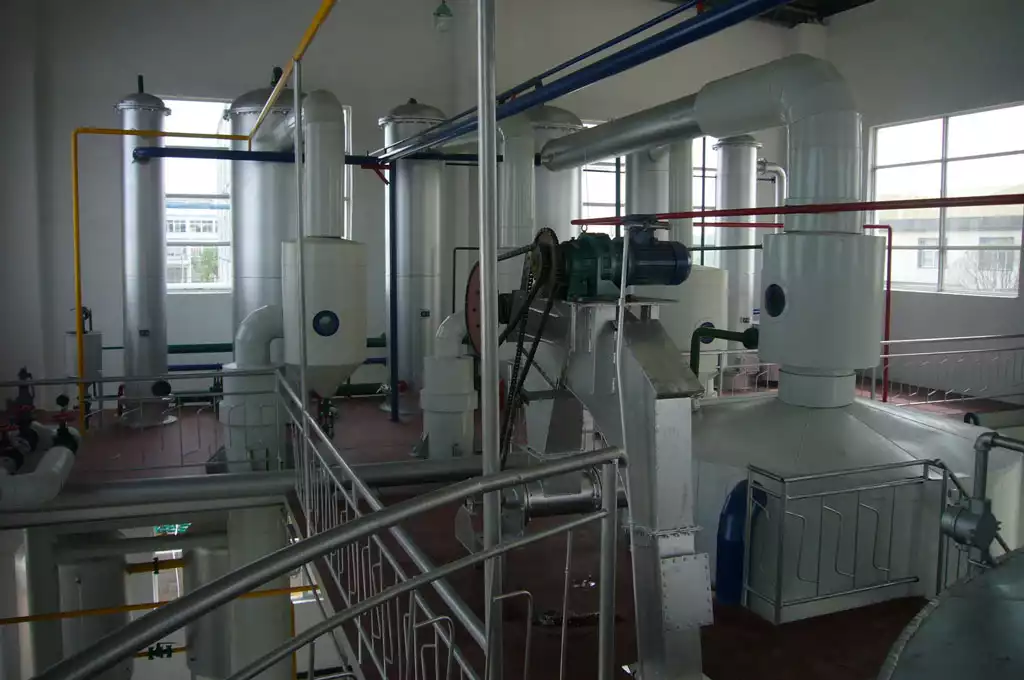
- Mixed Oil Evaporation
We can take advantage of the fact that oil is almost non-volatile, while the solvent has a low boiling point and is easy to evaporate. Use Coil steam heating to vaporize most of the solvent, thereby greatly increasing the concentration of oil in the mixed oil.
The specific process of mixed oil evaporation is: the mixed oil first enters the first long tube evaporator. The evaporated solvent enters the first steam condenser through the separation chamber. The concentrated mixed oil enters the second long tube evaporator for evaporation, and the evaporated solvent vapor enters the second steam condenser through the separation chamber. The solvent vapor coming out of the first and second evaporators does not contain water. It is cooled by the cold exchanger and flows directly into the circulating solvent tank.
This process mainly uses a long tube evaporator, characterized by a long heating pipeline. After preheating, the mixed oil enters the heating tube from the bottom, boils rapidly, and produces many steam bubbles that rise quickly. The rising steam bubbles drive and pull the mixed oil into a layer of liquid film along the tube wall, and the solvent continues to evaporate in this process. This thin film state enhances evaporation efficiency. - Distillation
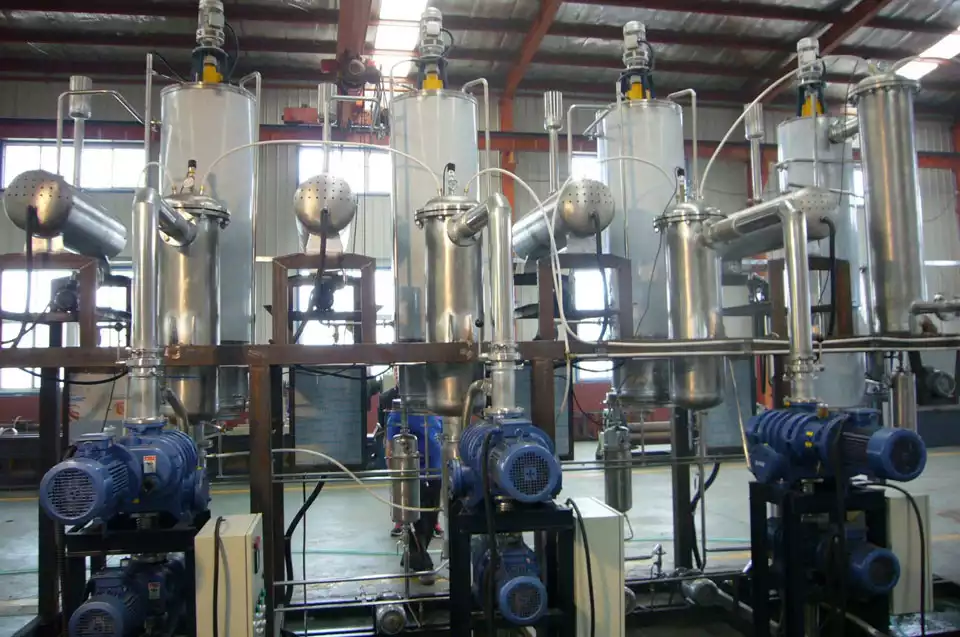
After the mixed oil evaporates, its concentration will increase. However, it still contains a small amount of solvent oil. We can use distillation to remove it.
Since mixed oil and water are not miscible, we can pass direct steam of a certain pressure into the concentrated mixed oil with a high boiling point (the amount of direct steam introduced is about 2% of the material amount).
At the same time, indirect steam into the jacket of the equipment for heating, so that the direct steam into the mixed oil will not condense.
When the pressure of the direct steam the solvent vapor and the external pressure balance, the solvent will boil, thereby reducing the boiling point of the high-boiling point solvent.
Finally, the uncondensed direct steam and the distilled solvent will enter the condenser together for condensation and recovery. The crude oil obtained after stripping enters the physical refining workshop for refining. - Wet Meal Desolventization
Because the wet meal separated by filtration in the extractor contains a small amount of solvent. Therefore, water vapor can be introduced into it for desolventization to remove the solvent. The principle is the same as mixed oil stripping.
The mixed vapor from the stripping tower and desolventization contains a small amount of water and enters the condenser. The condensed solvent and water mixture flow into the water separator for water separation, and the separated solvent flows into the circulating solvent tank. - Sedimentation and Filtration
Because rice bran crude oil contains insoluble impurity particles, mainly cake residue, mud, grass clippings, etc. Therefore, we can use the difference in specific gravity between them and oil to separate them by natural sedimentation.
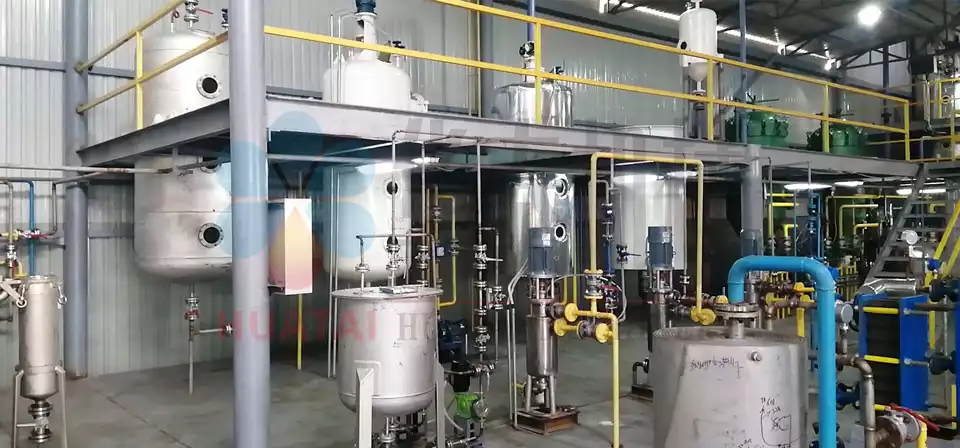
- Hydration Degumming
Add a small amount of water to the rice bran crude oil (the amount of water added is about 1%-3% of the weight of the crude oil) to make the water-soluble impurities therein condense precipitate and separate from the oil.
During hydration, the condensed and precipitated water-soluble impurities are mainly phospholipids. When the crude oil does not contain water or contains very little water, it can dissolve and disperse in the oil.
When phospholipids absorb water and moisten, water combines with the hydrophilic group of phospholipids, and has stronger hydrophilicity and stronger water absorption capacity.
With the increase of water absorption, the volume of phospholipid points gradually expands and condenses into colloid particles to form a colloid. Its weight is greater than that of oil, so it can precipitate from the oil. - Vacuum Drying
Because the rice bran oil after hydration degumming can contain a small amount of water. Therefore, we can use a continuous packing dehydrator for dehydration. In addition, the drying vacuum degree needs to reach about -0.09Mpa to facilitate the subsequent decolorization process.
- Adsorption Decolorization
The drying after rice bran oil enters the decolorization tank and fully contacts the adsorbent (white clay) under stirring to complete the adsorption equilibrium. After cooling, the adsorbent is separated by a filter press, and the filtered decolorized oil is then collected into the storage tank.
The adsorption decolorization time is about 30 minutes, and the amount of white clay added is about 2% of the oil weight. - Deacidification
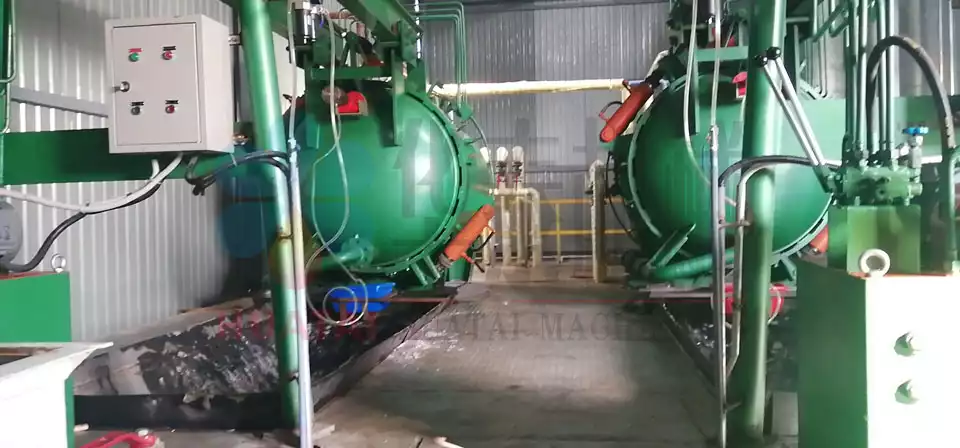
The decolorized rice bran oil passes through the oil heat exchanger, and then the heater is heated to about 250℃ and then enters the deacidification tower.
The deacidification tower is a structural packing tower. The rice bran oil flows downward and fully contacts with the saturated steam sprayed from the bottom to achieve the purpose of stripping deacidification.
The rice bran oil flows in the tower for about 5 minutes, and the direct steam consumption is 2% of the oil weight. - Deodorization
The deodorization tower is also a structural packing tower. The deacidified rice bran oil flows downward and fully contacts with the saturated steam stripping deodorization. The oil flows in the tower for about 15 minutes, the deodorization temperature is about 230℃, and the direct steam dosage is 1% of the oil weight.
- Dewaxing
Because the deodorized rice bran oil contains a small amount of bran wax, when the temperature is high, the bran wax dissolves in the oil in a molecularly dispersed state.
The deodorized rice bran oil is first sent to the crystallization tank for cooling and crystallization. Then the cooled oil passes through the filter press. Finally, the refined rice bran oil flows out and pours into the oil storage tank. The bran wax flows on the filter cloth, thereby achieving the purpose of oil-wax separation. - Filling
The finished rice bran oil obtained after refining is first temporarily stored in the oil storage tank. Then enters the filling production line, and it uses a small filling machine to fill and sell.
In general, the production method of rice bran oil mainly includes pretreatment, solvent extraction, wet meal desolventization, and rice bran crude oil refining. You can improve the extraction efficiency and quality of oil by reasonably selecting and optimizing these links, and achieve efficient and sustainable rice bran oil production.
Huatai Oil Machinery dedicates to the research development and manufacturing of rice bran oil production lines of various sizes (50-3000TPD) and provides integrated services such as customized solutions, transportation, installation, and after-sales. At present, we have established rice bran oil plants in Bangladesh, Thailand, Myanmar, Nigeria, Indonesia, Russia, Iran, and other countries, and have cooperated with them.
Get your best price
- Engineer quick quote
- The overall delivery speed is fast
- Financial choice
- Low installation costs and cost savings
30 years+ of oil mill plant R&D
More than 56 innovative technologies












