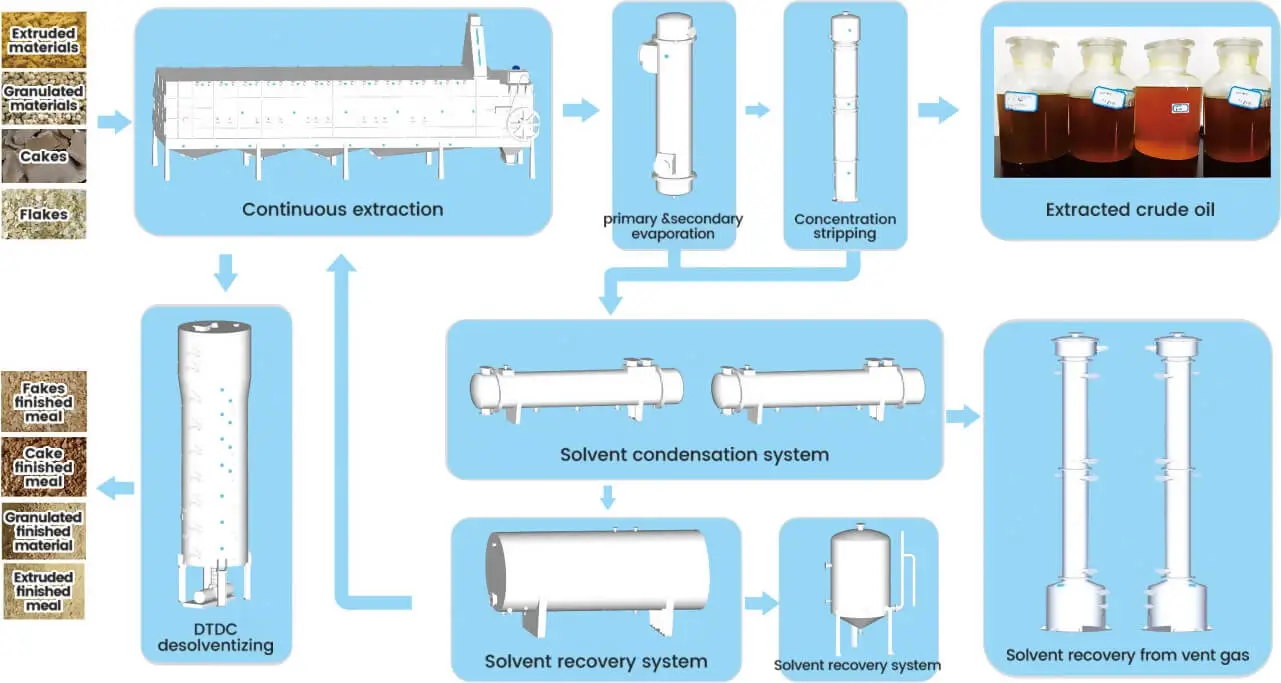
In the oil solvent extraction process, oilseed flakes or cakes from the solvent extraction stage are processed in an extraction plant. Here, a solid-liquid extraction technique is employed using a specific extractor that ensures the solvent thoroughly contacts and dissolves the oil. This results in a mixture called miscella and a byproduct known as wet meal. These are then sent to separate systems where the miscella undergoes evaporation to recover the solvent and produce crude oil, while the wet meal system recovers the solvent to yield the final extracted meal.
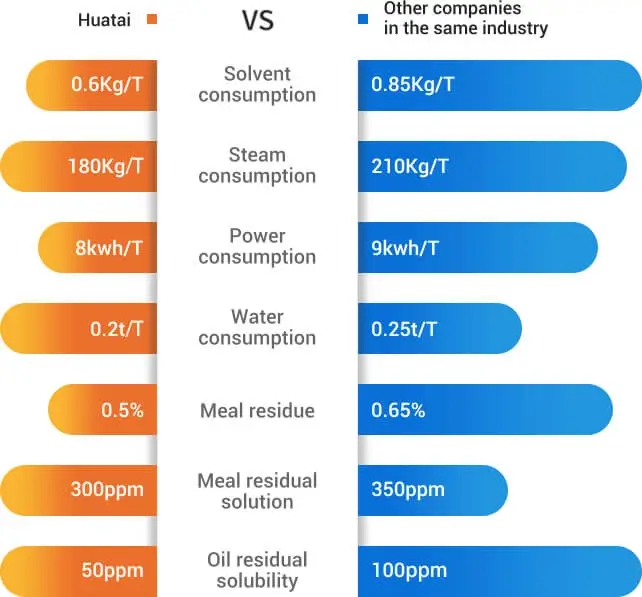
The oil solvent extraction plant is typically divided into four main sections: oil extraction, wet meal desolventizing, mixed oil evaporation, and solvent recovery. Post-extraction, the meal's residual oil content is impressively less than 1%.
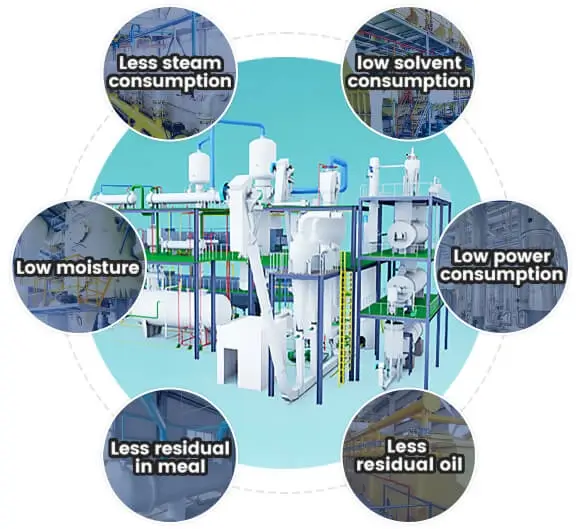
Efficient Steam Use: By carefully managing the use of steam exhaust water and exchanging heat with materials, the process significantly cuts down on steam consumption.
VRS Layer Benefits: The addition of a VRS layer through steaming and de-bonding helps to lower both the residual solvent in the meal and overall solvent usage.
Exhaust Gas Management: Implementing a well-designed exhaust gas absorption system effectively minimizes the solvent levels in the expelled gases.

Adaptable Equipment: The machinery in the extraction workshop is highly adaptable and capable of processing various materials. An automatic control system is in place to ease the workload of the staff.
Cost-Effective Evaporation: The evaporation system cleverly combines steam with a mechanical vacuum, which not only reduces production costs but also maintains the quality of the crude oil.
Reliable Components: The use of pumps and reducers from reputable brands decreases the likelihood of equipment malfunctions, enhancing workshop reliability.
Corn germ oil solvent extraction
Castor oil solvent extraction
Tea seed oil solvent extraction
Sesame oil solvent extraction
Safflower oil solvent extraction