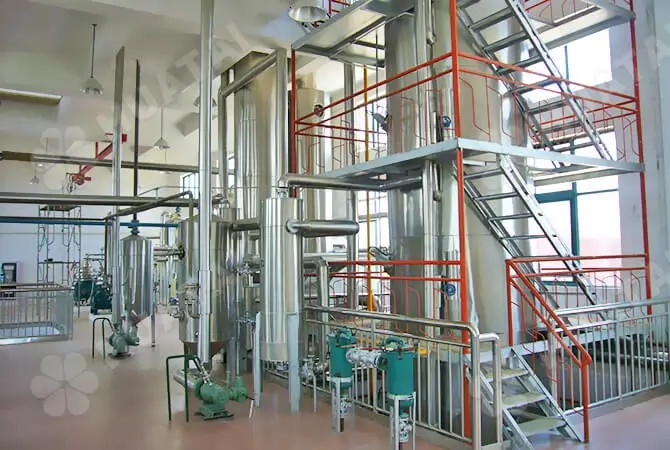
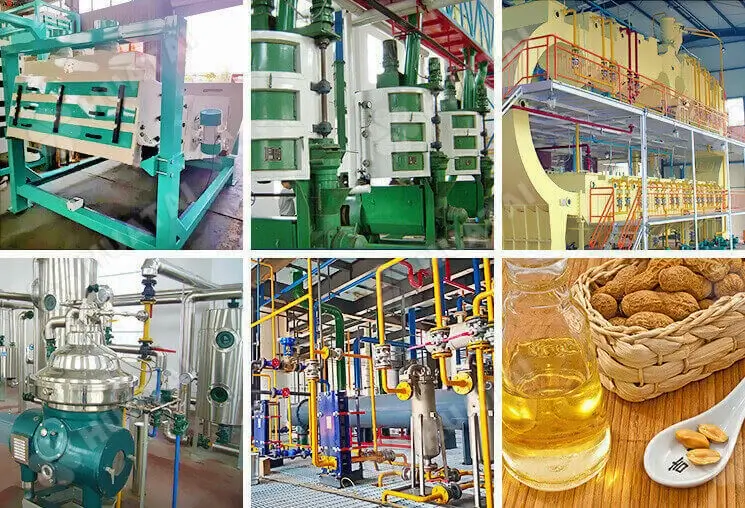
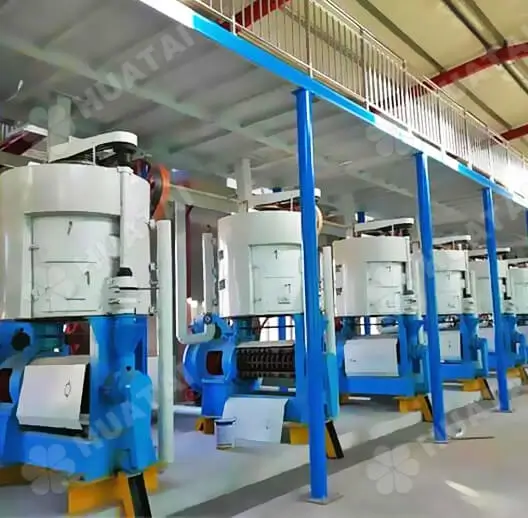
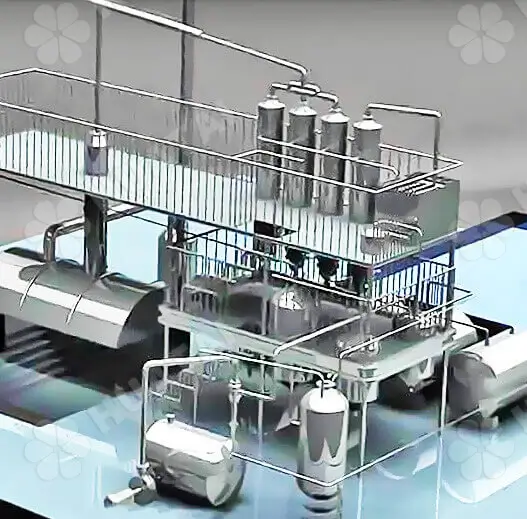
The peanut oil refining process effectively removes the impurities and harmful substances in the oil. Improves the quality and stability of the oil through the treatment of degumming, deacidification, decolorization, deodorization, and other steps.
Degumming: We usually use the acid refining method. The acid refining method is to add acid (such as phosphoric acid or citric acid) to make phospholipids and other impurities react and form precipitates, and then separate the precipitates by centrifuge.
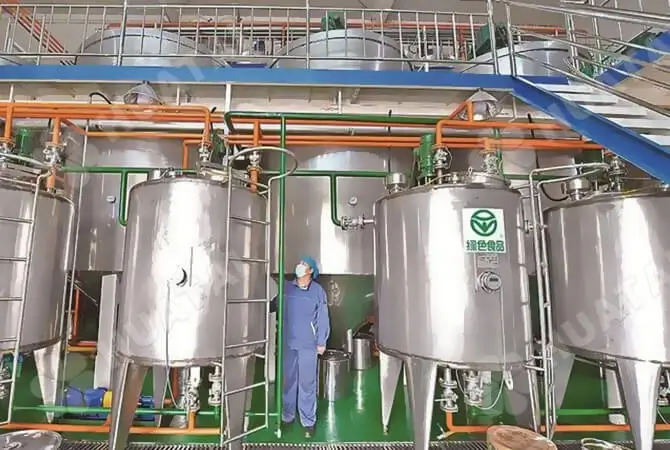
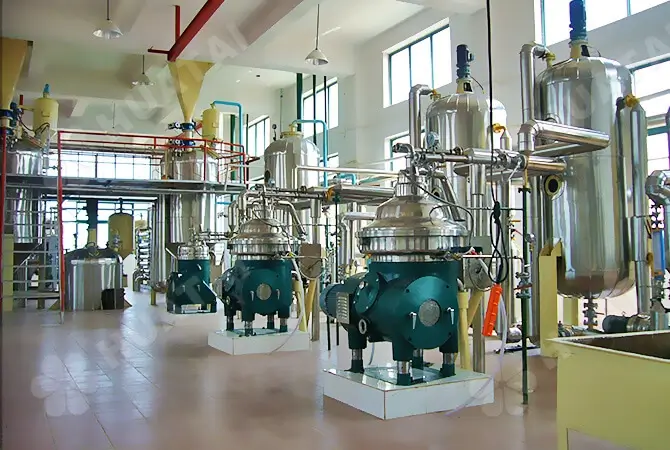


Deacidification: The main method used is food-grade lye neutralization. Add an appropriate amount of lye (such as sodium hydroxide solution) to peanut oil, so that the free fatty acids and alkali neutralization reaction occurs, resulting in soap foot (i.e., the main component of soap). Subsequently, the soap feet are separated by centrifugation, thus obtaining peanut oil after deacidification. This step not only effectively reduces the acidity of peanut oil, but also improves the stability and quality of the oil.
Decolorization: Add an appropriate amount of adsorbent, such as white clay, aluminum silicate, or activated carbon, to the deacidified peanut oil. These adsorbents can effectively adsorb the pigments and trace metal ions in the oil. The adsorbent and its adsorbed impurities are removed from the oil through filtration equipment, to get the decolorized oil with clear color and high purity.
Deodorization: The decolorized oil is heated and distilled under high temperature and high vacuum. During this process, odorants and volatiles evaporate with the steam and are discharged out of the system. After deodorization, peanut oil not only has a pure aroma but also has a much higher stability and is more conducive to storage and transportation.
Finally, the refined peanut oil is cooled, filled, and sealed through automated packaging equipment for storage and sale.